We never stop our research
and development.
CIJAN takes innovation as the core driving force and focuses on the research and development of automotive shock absorption technology. The company brings together industry elites to continuously overcome key technologies, successfully developing multiple leading products both domestically and internationally. Upholding the concept of high quality, CIJAN provides global customers with a safe and comfortable driving experience, leading technological innovation in the automotive shock absorber industry.





R&D center

R&D center

R&D center

R&D center

R&D center

Xichuan R&D Centre
Nanyang R&D Centre
Shanghai R&D Centre
Italy R&D Centre
Turin Innovation Centre
Core technology
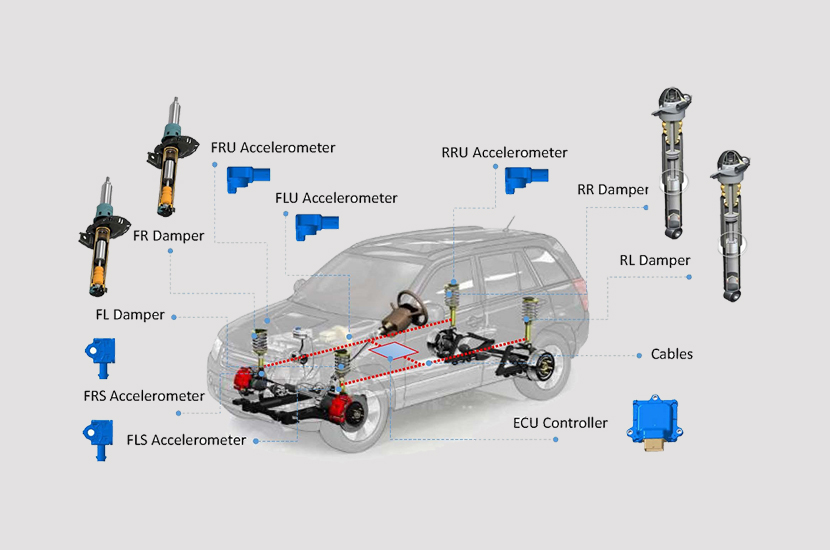
ADS Adaptive Damping System
An electronic control system collects signals related to the motion of the vehicle body and suspension through sensors. The controller calculates the optimal damping force and control current, which adjusts the damping force of the shock absorber by regulating the current to the electromagnetic valve. This system enhances both vehicle stability and ride comfort.
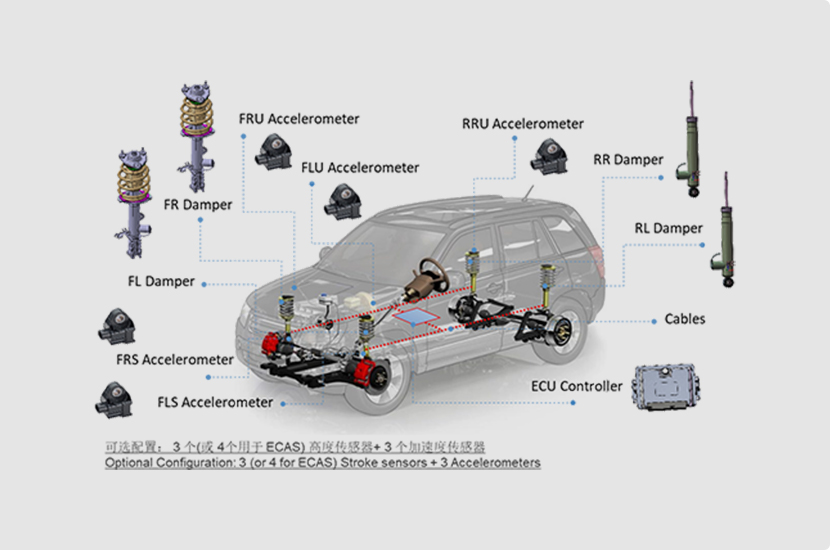
ECAS
The system consists of shock absorbers, air bags, controllers, air pumps, sensors, electromagnetic valves, and pipes. The controller determines the vehicle's status based on data from the height sensors and controls the operation of the air pump and electromagnetic valves to inflate or deflate the airbags, achieving adjustments to the vehicle height.
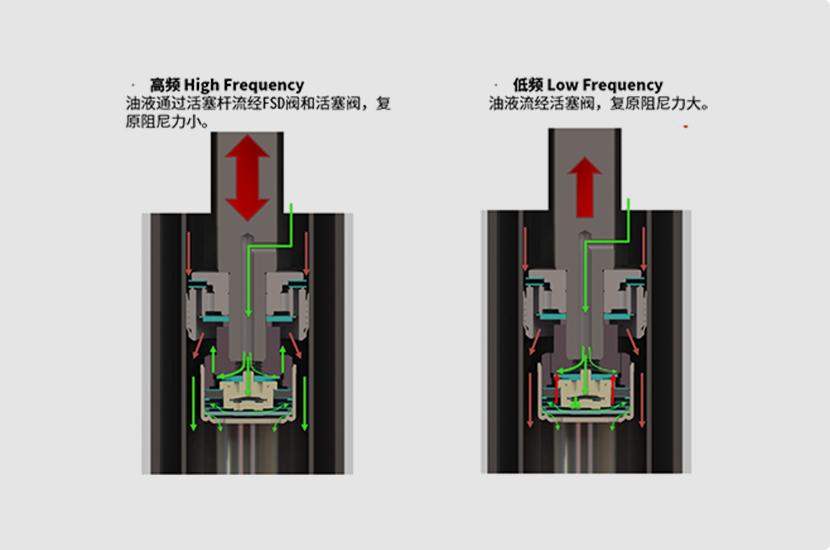
Frequency Adaptive Damper
The Frequency Adaptive Damper intelligently adjust their damping characteristics by real-time monitoring of vibration frequencies. It reduces damping forces during low-frequency vibrations to ensure comfort, while increasing damping forces during high-frequency vibrations to enhance stability. This adaptive regulation allows the dampers to cope with various road conditions, providing an exceptional driving experience for the vehicle.
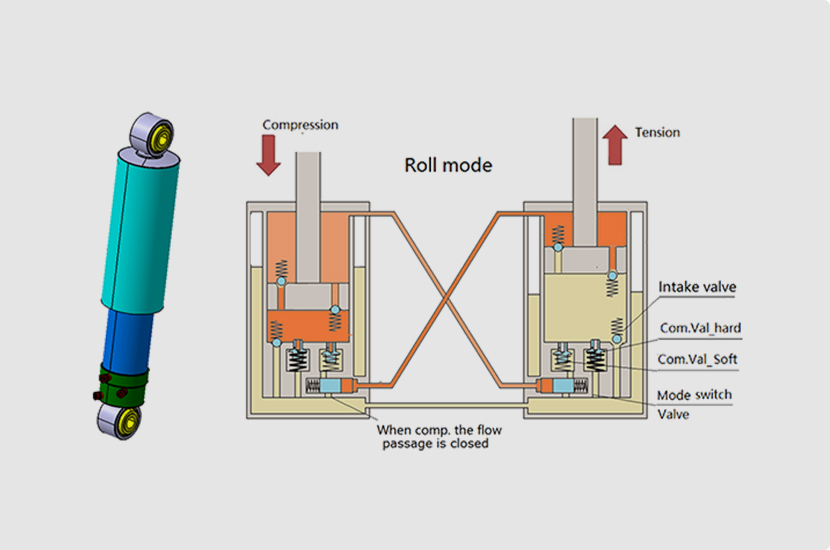
ARD anti-roll shock absorber
The upper and lower chambers of the dampers on both sides, as well as the oil reservoir chambers, are interconnected, enhancing damping force during vehicle roll and thereby improving vehicle stability.
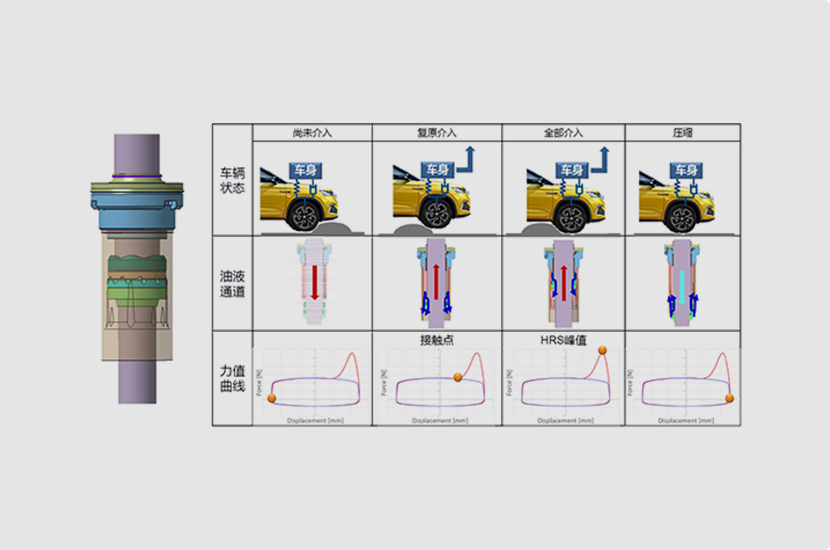
HRS hydraulic buffer
The hydraulic buffer structure of the damper consists of buffer cylinder sleeve, buffer cushion, floating piston and other components.Advantages of hydraulic buffer structure: compact structure, large energy absorption, smooth action, can effectively eliminate shock, vibration, noise and other harmful factors.
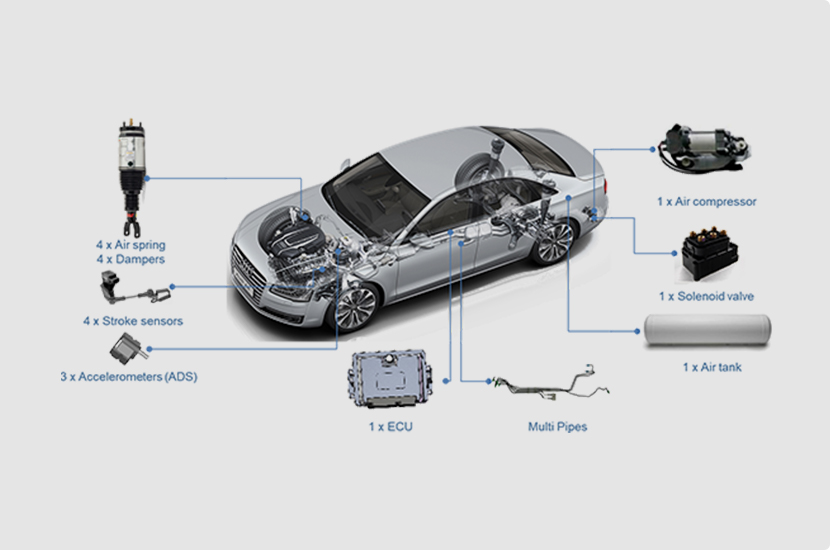
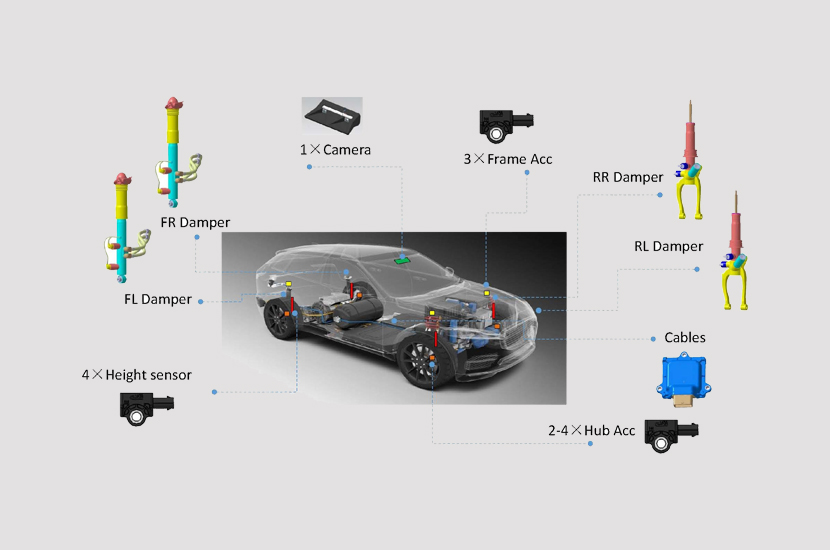
Full Active Suspension
Fully Active Suspension is a type of suspension system where both stiffness and damping coefficients can be adjusted in real-time based on operating conditions. The dampers in an active suspension can automatically adjust their damping characteristics in response to changes in vehicle load, road conditions or vibration levels, driving speed, and operating conditions such as acceleration, braking, and steering, in order to meet the optimal requirements for handling and comfort.
Magneto Rheological Damper
Magneto Rheological Damper utilizes the magnetorheological effect to respond in real-time to road conditions and driving environments based on input information from sensors monitoring the vehicle body and wheel movements. They feature continuously variable damping force, quick response, simple mechanical components, and low external energy input.